Cross-Margin and Isolated Margin in Futures Trading
Last updated November 4, 2024
In the dynamic world of futures trading, margin management is crucial for controlling risk and optimizing returns. Two primary margin modes are available to traders: Cross-Margin and Isolated Margin. Each mode offers distinct advantages and serves different trading strategies and risk management needs. In this article, we'll delve into the specifics of Cross-Margin and Isolated Margin and how to choose your preferred setting on Coinrule, helping you understand which option might be best suited for your trading style.
Coinrule users now have the option to choose between Isolated Margin Mode and Cross-Margin Mode when trading with futures. This added flexibility allows you to tailor your risk management strategies more precisely to your trading style and preferences.
What is Margin in Futures Trading?
Margin in futures trading refers to the collateral that traders must deposit to open and maintain positions. It acts as a safety net for brokers and exchanges to ensure that traders can cover potential losses. There are two types of margins to consider: initial margin and maintenance margin. The initial margin is the amount required to open a position, while the maintenance margin is the minimum amount that must be maintained in the account to keep the position open.
Cross-Margin Mode
Cross-Margin mode, also known as "spread margin," utilizes the entire margin balance in a trader’s account to cover potential losses. In other words, all positions share the same pool of margin, which can help in maintaining positions and avoiding liquidations during volatile market conditions.
Advantages of Cross-Margin
1. Efficient Use of Capital: By pooling all available funds, Cross-Margin allows traders to use their entire balance to cover potential losses, maximizing the capital available for maintaining positions.
2. Reduced Risk of Liquidation: During market volatility, having a larger pool of margin available can help prevent the liquidation of positions. Losses in one position can be offset by gains or available margin from other positions.
3. Flexibility: Cross-Margin is particularly useful for traders with multiple positions as it offers more flexibility and better capital utilization.
Disadvantages of Cross-Margin
1. Higher Risk: Since all positions share the same margin, a significant loss in one position can affect the entire account balance, potentially leading to a margin call or liquidation of other positions.
2. Complexity: Managing risk can be more complex with Cross-Margin, especially for traders with diverse and large portfolios.
Isolated Margin Mode
Isolated Margin mode allocates a specific amount of margin to each individual position. The margin allocated to a particular position is isolated, meaning that the potential loss is limited to the margin set aside for that position alone.
Advantages of Isolated Margin
1. Controlled Risk: By isolating the margin for each position, traders can limit potential losses to the allocated amount, providing better risk management.
2. Simplified Management: Each position is independent, making it easier to manage and monitor individual trades without worrying about the impact on the overall account balance.
3. Strategic Allocation: Traders can allocate different amounts of margin to different positions based on their confidence and risk tolerance for each trade.
Disadvantages of Isolated Margin
1. Risk of Liquidation: Since each position has its own margin, there is a higher risk of liquidation if the market moves against a particular trade, as it does not have access to the broader pool of funds.
2. Capital Inefficiency: Isolated Margin can be less efficient in terms of capital utilization, as excess margin in one position cannot be used to support another.
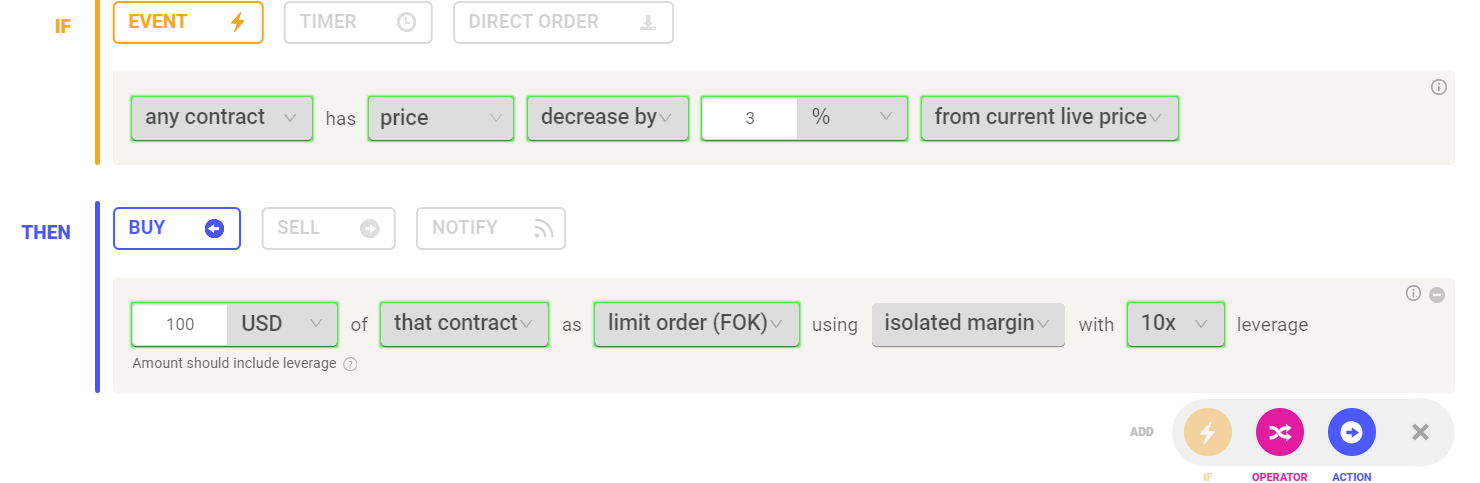
How to Use Set Your Margin Mode on Coinrule
- Navigate to 'Create Rule' page
- Select your preferred Futures Exchange e.g. Binance Futures
- When setting up your trading rule, you will see the option to select either Isolated Margin Mode or Cross-Margin Mode.
- Choose the margin mode that best fits your risk management strategy for each trade.
Choosing Between Cross-Margin and Isolated Margin
The choice between Cross-Margin and Isolated Margin depends on your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and portfolio management preferences.
Use Cross-Margin If:
- You have a diversified portfolio with multiple positions.
- You want to maximize capital efficiency and reduce the risk of liquidation.
- You are comfortable managing a pooled margin account and the associated complexities.
Use Isolated Margin If:
- You prefer to limit risk on individual positions.
- You want simpler risk management with independent positions.
- You are trading with a high-risk strategy on specific positions and want to protect your broader account balance.
Conclusion
Both Cross-Margin and Isolated Margin offer unique benefits and cater to different trading needs. Understanding the differences and advantages of each can help you make more informed decisions and improve your trading performance. As always, it's essential to align your margin strategy with your overall trading goals and risk management practices.
By mastering the use of these margin modes, you can enhance your trading experience and better navigate the complexities of the futures market.
Happy trading!